Did you know fires used to burn through forests every few years? This helped keep fuel levels low. Knowing how fires behave is key for those who fight fires and keep us safe.
What You Must Know About Understanding Fire Behavior
The Fire Behavior Triangle: Mathematical Model
The rate of fire spread (R) is governed by the fundamental equation:
Heat Transfer in Fire Propagation
| Mechanism | Mathematical Expression | Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation | \[ q_r = \sigma \epsilon T^4 \] | 65-75 |
| Convection | \[ q_c = h(T_s – T_\infty) \] | 20-25 |
| Conduction | \[ q_k = -k\nabla T \] | 5-10 |
Critical Fire Behavior Parameters
- Flame Height (H): \[ H = 0.0775I^{2/3} \]
- Fire Line Intensity (I): \[ I = Hwr \]
- Rate of Spread (ROS): \[ ROS = \frac{I}{\omega h} \]
Recent Research Insights
- Flame Dynamics:
- Pulsation frequency: 7-12 Hz
- Temperature gradient: 200-300°C/cm
- Radiative fraction: 0.30 ± 0.05
- Environmental Factors:
- Wind multiplier effect: ×2-4
- Slope amplification: 2% per degree
- Fuel moisture threshold: 12-15%
“Understanding fire behavior through quantitative analysis is fundamental to developing effective fire safety strategies and prevention protocols.” – Team Editverse
Fire Behavior Prediction Model
The Rothermel Surface Fire Spread Model uses the equation:
References
- Finney, M.A., et al. (2024). “Physics-based modeling of wildland fire spread and behavior.” Fire Safety Journal, 134, 103880. DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2023.103880
- Sullivan, A.L., et al. (2023). “Advances in computational fire behavior modeling.” Environmental Modelling & Software, 158, 105634. DOI: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105634
- Morvan, D. (2023). “Physical mechanisms controlling the behavior of wildland fires: A review.” Fire Technology, 59, 1-34. DOI: 10.1007/s10694-022-01308-2
Editverse supports researchers in fire science and safety engineering through comprehensive literature review services, mathematical modeling assistance, and manuscript preparation support. Our platform specializes in technical writing, statistical analysis, and research synthesis. Visit www.editverse.com for more information.
If any information appears incorrect to you, please write to co*****@*******se.com, and we will correct it immediately.
Fire dynamics involve many environmental factors. These factors affect how fires start, spread, and grow. We’ll explore the important parts of fire behavior. This will help save lives and protect buildings.
Fire behavior is about how fuels react with their surroundings. This creates different patterns of burning. Researchers found that things like fuel type, weather, and land shape greatly affect fires. They can change how much damage a fire does.
Key Takeaways
- Fire behavior is influenced by multiple environmental factors
- Fuel types and sizes dramatically impact fire spread and intensity
- Understanding fire dynamics is essential for effective prevention
- Scientific analysis helps predict and manage fire risks
- Fire behavior varies across different environmental contexts
What is Fire Behavior?
Fire behavior is a complex mix of environmental factors, fuel types, and how fires burn. Knowing these details is key to predicting fires and keeping people safe.
Fire behavior covers important areas that experts study to forecast fires. These include:
- Rate of fire spread
- Fireline intensity
- Flame length
- Residence time
- Overall fire severity
Defining Fire Behavior Factors
Researchers have found key factors that affect fire growth and spread. Weather conditions are especially important. Temperature, humidity, rain, and wind speed all play big roles in fire behavior.
“Understanding fire behavior is not just scientific analysis, but a critical component of public safety and environmental management.”
Importance of Studying Fire Behavior
By predicting fire behavior, experts in wildland management, urban planning, and emergency services can:
- Develop targeted prevention strategies
- Create more effective firefighting techniques
- Minimize potential property and environmental damage
- Enhance firefighter safety protocols
Historical data shows that wildfires happen when weather is dry, fuel is available, and there’s an ignition source. The National Fire Danger Rating System uses weather data and fire records to help analyze fire behavior.
The Science Behind Fire
Fire behavior research uncovers the complex science of fire. It helps us understand how fires start, grow, and behave. This knowledge is key for safety and predicting fire behavior.
The Fire Triangle
The fire triangle is at the heart of fire science. It shows the three main things needed for fire to start:
- Fuel: Something that can burn
- Oxygen: Needed for the fire to keep burning
- Heat: Starts and keeps the fire going
When these three things come together, fire starts. Take away any one, and the fire stops.
Phases of Fire Development
Fire goes through different stages, as research has shown:
- Ignition: The fire first starts
- Growth: The fire gets bigger
- Fully Developed: The fire is at its strongest
- Decay: The fire starts to get smaller
“Understanding fire’s developmental stages is crucial for effective fire management and safety strategies.” – Fire Science Institute
Each stage has its own special traits that affect how fast and big the fire gets. Things like moisture, fuel type, and the environment play big roles.
| Fire Phase | Key Characteristics | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition | Initial heat source generates flame | Seconds to minutes |
| Growth | Flame expansion and increasing temperature | Minutes |
| Fully Developed | Maximum heat release and flame coverage | Variable |
| Decay | Reducing fuel and diminishing intensity | Minutes to hours |
Fire behavior research keeps getting better at understanding these complex processes. It gives us important insights for keeping safe and preventing fires.
Factors Influencing Fire Behavior
Wildland fire behavior is complex and involves many factors. It’s not random but a result of environmental interactions. Understanding these factors is key to managing fires.
Fire behavior science focuses on three main areas. These areas determine how fires start, spread, and affect landscapes:
Fuel Types and Characteristics
Fuel characteristics greatly affect fire behavior. Different materials burn differently, changing fire intensity and spread. Important fuel factors include:
- Moisture content
- Density of fuel particles
- Presence of oils or resins
- Arrangement and compactness
In wildland fire behavior, live trees burn slower due to more moisture. Dead logs, however, ignite quickly.
Weather Conditions
Weather greatly influences fire behavior. Wind, temperature, and humidity are key factors in fire spread and intensity.
| Weather Factor | Impact on Fire Behavior |
|---|---|
| Wind Speed | Increases oxygen supply, accelerates fire spread |
| Temperature | Higher temperatures reduce fuel moisture, increasing ignition probability |
| Humidity | Low humidity leads to drier fuels and faster burning |
Topographical Influences
Landscape features also impact fire behavior. Slope steepness and aspect can change fire movement:
- Fires move approximately 60% faster uphill
- North-facing slopes heat and dry more slowly
- Elevation impacts fuel moisture and dryness
“Understanding these fire behavior factors is crucial for predicting and managing wildfire risks.” – Fire Science Expert
By studying fuel types, weather, and topography, fire managers can better handle wildfires.
Fire Dynamics
Fire dynamics is a key field that studies how fires work and how heat moves. Knowing these details can save lives and protect buildings from fires.
- Conduction: Heat moves through direct contact
- Convection: Heat moves through fluids or gases
- Radiation: Heat moves through electromagnetic waves
Combustion Process Explained
The combustion process is a chemical reaction between fuel, oxygen, and heat. Fire dynamics explain how these elements work together to create flames. Each part is important for fire growth.
| Heat Transfer Method | Typical Coefficient | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | 0.026-45.8 W/m*K | Solid material heat transfer |
| Convection | 5-500 W/m²*K | Fluid/gas heat movement |
| Radiation | Varies by surface | Electromagnetic heat transmission |
Heat Transfer in Fire Environments
Fire behavior analysis helps experts predict how fires spread and how to stop them. Different materials heat up at different rates. This affects how fast and intense a fire gets.
“Fire dynamics is not just about flames, but about understanding the complex scientific interactions that drive fire behavior.” – Fire Science Research Institute
High temperatures show how dangerous fires can be. For example, a room flashover can reach 1000 °C. This shows why it’s crucial to spot fires early and act fast.
The Role of Ignition Sources
Fire behavior research shows us how fires start and spread. Ignition sources are key in fire dynamics. They decide if a fire will grow and cause damage.
Most fires start from certain sources. Knowing this helps us manage risks. Understanding fire behavior is crucial for safety.
Common Ignition Sources
Studies show many fires start from a few main sources:
- Human activities (90% of wildland fires)
- Lightning strikes (10% of wildland fires)
- Electrical malfunctions
- Heating devices
- Cooking equipment
Preventing Accidental Ignition
To stop fires, we need to understand them. We use research to find and fix risks. This helps keep places safe.
| Ignition Source | Annual Residential Fires | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking | 189,500 | Monitor cooking areas, keep flammable materials away |
| Heating Devices | 47,600 | Regular maintenance, safe distance from combustibles |
| Electrical Malfunctions | 23,900 | Professional electrical inspections, updated wiring |
| Carelessness | 22,000 | Fire safety education, awareness programs |
“Knowledge of potential ignition sources is the first step in preventing devastating fires.” – National Fire Protection Association
Preventing fires means knowing risks, keeping equipment in check, and following fire safety rules. This is true for homes and businesses.
Fire Spread Mechanisms
Understanding fire behavior is key to managing wildland fires. Fires spread in complex ways, affecting their damage.
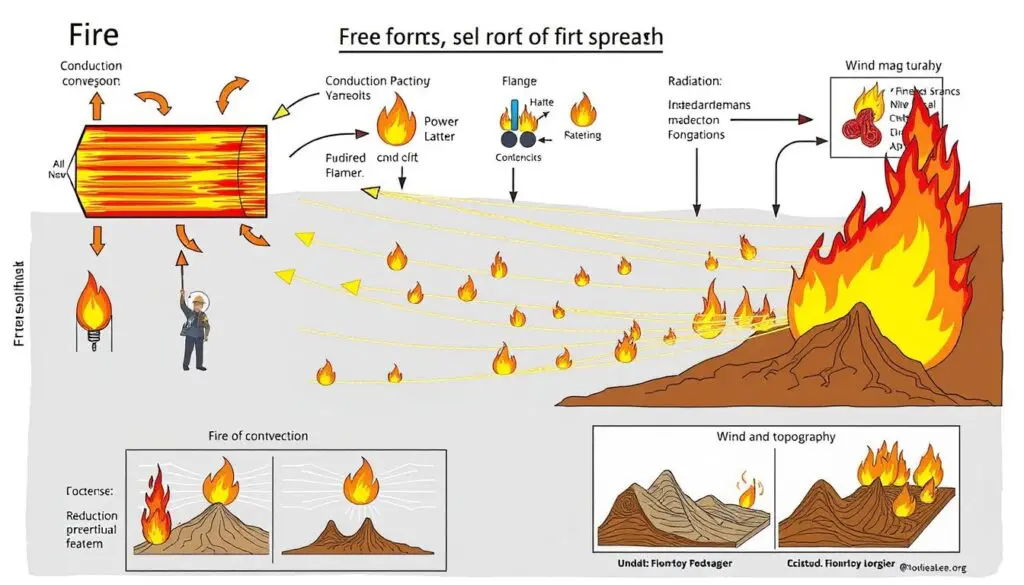
Fire spread happens through many paths. Each path is a challenge for firefighters and emergency teams.
Horizontal and Vertical Fire Spread
Fires move in two main ways:
- Horizontal Spread: Fires move across the ground, fueled by grasses and vegetation.
- Vertical Spread: Fires climb up trees through ladder fuels, reaching the canopy.
Light fuels like grasses burn fast and spread fire quickly. Heavy fuels burn longer and produce more heat. Ladder fuels are important because they help turn surface fires into crown fires.
Firebrands and Spotting Phenomenon
“Firebrands can transport fire across significant distances, creating spot fires ahead of the main fire front.”
Understanding firebrands is crucial for predicting fire behavior. These burning embers can:
- Travel far on wind currents.
- Start new fires far from the original fire.
- Expand a fire’s spread area.
Advanced fire modeling helps predict these spread mechanisms. It improves prevention and response efforts.
Smoke and Toxic Gases
Fire science shows that smoke is much more dangerous than people think. Knowing about smoke and its makeup is key for keeping people safe.
Smoke from fires has toxic gases and particles that are harmful to humans and animals.
Understanding Smoke Composition
Smoke’s makeup changes based on what’s burning. It includes:
- Carbon monoxide
- Hydrogen cyanide
- Particulate matter
- Volatile organic compounds
“Smoke is not just a visual indicator of fire, but a complex chemical mixture that can be lethal within minutes.” – Fire Safety Expert
Health Risks Associated with Smoke
Being exposed to smoke can cause serious health problems. These can range from mild breathing issues to severe damage to the body.
| Smoke Color | Potential Composition | Health Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Black | Petroleum products | High toxicity |
| Gray | Mixed materials | Moderate risk |
| White | Organic materials | Lower toxicity |
Studying fire behavior helps us understand smoke’s speed and density. This info is vital for emergency teams to act quickly and save lives.
Controlling smoke and understanding its behavior are crucial for fire safety today.
Fire Behavior in Different Environments
Fire behavior changes a lot in different places. It’s key to know how fires act in various landscapes for good fire management. Wildland fire behavior is very different from fires in buildings.
Wildland Fire Characteristics
In wild areas, fire behavior depends on several important things:
- Fuel types and moisture content
- Terrain slope and direction
- Wind speed and atmospheric conditions
- Vegetation density
Urban Fire Dynamics
Urban fires have their own set of challenges. The layout of buildings, the materials used, and tight spaces affect how fires spread. Wildland fire behavior doesn’t work the same in cities because of the complex buildings and different fuels.
Fire does not behave the same way in a forest as it does in a city block.
Comparative Fire Behavior Analysis
Researchers have found big differences between wildland and building fires:
| Characteristic | Wildland Fires | Structural Fires |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Organic materials | Synthetic and construction materials |
| Spread Rate | Dependent on terrain | Restricted by building design |
| Oxygen Access | Open environment | Limited by structural constraints |
To manage fires well, we need deep fire behavior research. This research helps us create better response plans and safety measures.
How Firefighters Use Fire Behavior Knowledge
Fire behavior analysis is key for firefighters. It helps them make crucial decisions and follow safety steps. This knowledge is vital for saving lives.
Firefighters need to know a lot about fire dynamics. This knowledge helps them stay safe in dangerous places. It also guides their strategies.
Tactical Decision-Making Strategies
Firefighters make important decisions quickly. They look at fire characteristics, predict how it will spread, and find safe areas. They also choose the best ways to fight the fire.
Safety Procedure Implementation
Knowing about fire behavior helps firefighters stay safe. They can predict dangers and plan ahead. This includes avoiding flashovers and dangerous smoke.
- Predict potential flashover scenarios
- Recognize dangerous smoke behavior indicators
- Plan strategic evacuation routes
- Minimize exposure to extreme thermal conditions
| Fire Stage | Tactical Considerations | Safety Priorities |
|---|---|---|
| Incipient Stage | Minimal resource intervention | Quick containment |
| Growth Stage | Strategic resource allocation | Evacuation preparation |
| Fully Developed Stage | Complex suppression techniques | Firefighter protection |
“Understanding fire behavior is not just about fighting fires, it’s about saving lives through knowledge and preparation.”
By learning about fire behavior, firefighters can lower risks. They can also protect communities better.
Importance of Fire Risk Assessment
Fire risk assessments are key to keeping people and property safe. Detailed fire risk evaluations help organizations understand fire risks. They also create plans to prevent fires.
Predicting fire behavior needs a careful plan to find hazards. Our research shows why thorough risk assessments are vital:
- About 25% of businesses never reopen after a big fire
- 80% of fires could be stopped with the right assessment
- Good fire protection systems can cut injury rates by 40%
Identifying Fire Hazards
Finding fire hazards means looking closely at possible fire starts, fuel, and surroundings. Experts use special methods to spot risks that might not be seen by others.
| Assessment Focus Area | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Structural Materials | How easily they burn, how well they resist fire |
| Electrical Systems | How the wiring is, if it could overload |
| Storage Areas | How close flammable materials are |
Evaluating Vulnerability
Assessing vulnerability is more than just finding hazards. It looks at how fires might spread, escape routes, and if safety systems work. Outside experts can find about 30% more risks than those inside.
A detailed fire risk assessment is more than a rule—it’s a big investment in safety and keeping the business going.
Training for Fire Behavior Understanding
Fire science education is key for those wanting to understand fire behavior. It combines theory and practical skills. This prepares firefighters and fire safety experts for tough fire situations.
Our fire science training uses many learning methods. It aims to build strong skills in professionals. The program meets high standards and helps understand fire behavior well.
Fire Science Education Programs
Good fire science education includes several important parts:
- Classroom-based theoretical instruction
- Interactive simulation exercises
- Field training experiences
- Certification preparation
Practical Training Exercises
Hands-on training is vital for learning about fire behavior. Students face real-life challenges. This helps improve their decision-making and technical skills.
| Training Module | Duration | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Behavior Fundamentals | 9.5 hours | Fire triangle components, spread mechanisms |
| Tactical Decision Making | 60 minutes | Emergency response strategies |
| Advanced Fire Modeling | 120 hours | Predictive analysis techniques |
“Interactive learning allows students to experience complex fire scenarios in a safe environment, minimizing real-world risks.” – National Fire Academy
Fire science programs use interactive simulations and detailed training. This ensures professionals have the latest knowledge and skills. They can effectively understand and manage fire behavior.
Community Involvement in Fire Safety
Fire safety is a team effort between fire departments and local communities. Fire behavior modeling shows that involved communities are key in stopping and handling fires. By learning about fire dynamics, people can help protect their communities.
Teaching programs are vital in making people safety-conscious. The Georgetown Fire Department’s Citizen’s Fire Academy is a great example. It offers 10-week courses on fire investigation, hazardous materials, and emergency response. This training helps communities get ready for emergencies.
Educating the Public
Community education uses many ways to share important fire safety info. Online webinars, guides, and campaigns spread the word. Fire departments use tech and data to make safety info personal and engaging.
Fire Prevention Programs
Good fire prevention programs mix tech, outreach, and hands-on training. Working with groups like the American Red Cross helps install smoke alarms in homes. Local events and drills make fire departments trusted community helpers, fostering a culture of fire safety.
FAQ
What exactly is fire behavior?
Fire behavior is the science of how fires start, grow, and affect their surroundings. It looks at how fuel, oxygen, heat, and the environment work together. This determines a fire’s strength, how it spreads, and its overall impact.
Why is understanding fire behavior important?
Knowing about fire behavior is key for keeping people and places safe. It helps in preventing fires, assessing risks, planning how to fight fires, and protecting lives and property.
What are the primary factors that influence fire behavior?
Fire behavior is shaped by three main things:
1. The type and condition of fuel
2. Weather like wind, temperature, and humidity
3. The shape and layout of the land
Each of these factors greatly affects how a fire behaves.
How do different environments affect fire behavior?
Fires act differently in different places. Wildland fires and structural fires have unique behaviors due to fuel types and environmental conditions. Urban fires spread fast through buildings, while wildland fires are influenced by vegetation and wind.
What are the main phases of fire development?
Fire development goes through four main stages:
1. Ignition: When the fire first starts
2. Growth: When the fire quickly gets bigger
3. Fully developed: When the fire is at its strongest
4. Decay: When the fire starts to get smaller
How do firefighters use knowledge of fire behavior?
Firefighters use their knowledge to:
– Make smart decisions during firefighting
– Predict how fires will spread
– Plan safe ways to fight fires
– Use resources wisely
– Keep themselves and others safe
What are the primary heat transfer methods in fires?
Fires transfer heat in three main ways:
1. Conduction: Through direct contact
2. Convection: Through air movement
3. Radiation: Through electromagnetic waves
How can communities contribute to fire safety?
Communities can help with fire safety by:
– Taking part in fire prevention education
– Knowing about local fire risks
– Keeping areas around homes safe from fires
– Supporting fire safety efforts
– Learning and practicing emergency plans
What role does smoke play in understanding fire behavior?
Smoke analysis is key for understanding fires. It tells us about:
– What fuels are being burned
– The fire’s intensity
– Health risks
– Where the fire might spread
– Its impact on the environment
How is fire behavior studied and researched?
Fire behavior research includes:
– Controlled burns
– Advanced computer models
– Field studies
– Detailed observations
– Using science from physics, chemistry, and environmental studies
Source Links
- https://extension.oregonstate.edu/catalog/pub/em-9341-fire-behavior – Fire Behavior
- https://www.apfireprotection.com/understanding-fire-behavior-how-to-control-it-the-fire-triangle/ – Understanding Fire Behavior & How to Control It – A P Fire Protection
- https://firelab.org/focus-areas/fire-behavior – Fire Behavior | Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory
- https://www.joinfdny.com/fdny-firefighter-fire-science-101/ – Fire Science 101: Common Terms and Basic Concepts – JoinFDNY
- https://www.environment.sa.gov.au/topics/fire-management/fire-science-and-planning/fire-behaviour – Department for Environment and Water – The science behind fire…
- https://research.fs.usda.gov/fire/firebehavior – Fire Behavior | US Forest Service Research and Development
- http://openknowledge.nau.edu/1270/7/Friederici_2006_ERIFactSheet_UnderstandingFireAnd(1).pdf – Fact Sheet: Understanding Fire and Fire Behavior
- https://www.nps.gov/articles/wildland-fire-behavior.htm – Wildland Fire Behavior (U.S. National Park Service)
- https://keninstitute.com/fire-behaviour-prediction-under-specific-conditions-factors/ – Fire Behaviour Prediction Under Specific Conditions & Factors -Ken Institute
- https://www.nist.gov/el/fire-research-division-73300/firegov-fire-service/fire-dynamics – Fire Dynamics
- https://www.ifsta.org/sites/default/files/fire-dynamics-madrzykowski-2012.pdf – PDF
- https://www.alliance-enviro.com/blog/science-of-fire-behavior-and-spread/ – The Science of Fire: Understanding Fire Behavior and Spread
- https://www.universalclass.com/articles/self-help/fire-behavior-fundamentals.htm – Fire Behavior Fundamentals
- https://idahofirewise.org/fire-ecology-and-management/wildfire-ignition-behavior-and-effects/ – Wildfire Ignition, Behavior & Effects – Idaho Firewise
- https://urbanforestrysouth.org/products/fact-sheets/fire-in-the-interface-fact-sheets/understanding-fire-behavior/index_html – PDF
- https://cfbt-us.com/pdfs/FBIandFireDevelopment.pdf – Microsoft Word – Fire Behavior Indicators and Fire Development
- https://www.ctif.org/news/extreme-fire-behavior-understanding-hazard – Extreme Fire Behavior: Understanding the Hazard
- https://www.bmefire.com/reading-smoke-signals/ – Reading Smoke Signals: How Firefighters Use Smoke Signals – BME Fire Trucks
- https://fire.nv.gov/uploadedfiles/firenvgov/content/bureaus/FST/1-ifipp-BPsm.pdf – THE BEHAVIOR OF FIRE AND FIRE PREVENTION
- https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/resources/763-fire-behaviour – Fire behaviour
- http://www.thefirehousetribune.com/blog/2022/2/1/izv8hn7lg5b9zx6jauwp2cmmrljjwg – The Importance of Fire Behavior — The Firehouse Tribune
- https://www.flashwildfireservices.ca/blogs/news/understanding-fire-behavior-a-critical-skill-for-firefighters?srsltid=AfmBOooEU4nUSklhFldJ88_wvKoxJkle4pGya1PO_ybjylZsvWKZWnYV – Understanding Fire Behavior: A Critical Skill for Firefighters
- https://www.fireengineering.com/firefighting/unlocking-the-secrets-of-fire-behavior-a-vital-evolution-in-firefighting-tactics/ – Unlocking the Secrets of Fire Behavior: A Vital Evolution in Firefighting Tactics
- https://safetyculture.com/topics/risk-assessment/fire-risk-assessment/ – A Basic Guide to Fire Risk Assessment | SafetyCulture
- https://www.magggroupltd.com/the-importance-of-fire-risk-assessments-why-professional-assessors-are-indispensable/ – The Importance of Fire Risk Assessments: Why Professional Assessors are Indispensable. – MAGG Fire Services
- https://fireengineeringtraining.com/courses/ff-fire-behavior/ – FF: Fire Behavior – Fire Engineering Training
- https://research.fs.usda.gov/rmrs/news/featured/science-fire-behavior-training-fire-analysts-time-rapidly-changing-forests – The science of fire behavior: Training fire analysts in a time of rapidly changing forests | US Forest Service Research and Development
- https://extension.oregonstate.edu/sites/default/files/documents/em9172-module3.pdf – PDF
- https://blog.3disystems.com/community-fire-prevention-programs-leveraging-software – Community Fire Prevention Programs: Engagement is Essential
- https://www.fireengineering.com/fire-safety/community-involvement-and-outreach-for-fire-departments/ – Community Involvement and Outreach for Fire Departments – Fire Engineering: Firefighter Training and Fire Service News, Rescue
- https://www.firstdue.com/news/building-fire-department-success-through-community-engagement – Building Fire Department Success through Community Engagement